Cost Allocation Overview
Cost Allocation is an automated function to allocate of indirect costs, direct costs or revenues based on a user-defined plan of where to allocate from, where to allocate to, and how much to allocate. The defined allocation structure is ultimately used by the system to compute and post the allocation. Before the actual posting, the system process presents the allocation in a reportable fashion to verify the setup and results.
Cost Allocation is the concept of allocating from pool chart of account distributions to base chart of account distributions. At the time costs or revenues are initially recorded, the ultimate chart of account distribution is not yet known or the portions attributable to multiple distributions are not known. As a result, the activity is recorded against a 'pool’ distribution. At a later stage, that activity can be allocated to the ultimate base distributions.
There are several features described in the Cost Accounting User Guide serve to reduce the need for cost allocations, but even with these features, the need to use Cost Allocation is never eliminated:
-
Front and Back End Split functionalities allocate costs in real-time and by timely system processing, respectively.
-
Overhead allocates indirect costs based on direct costs when a Major Program has an agreement with a funding source for the reimbursement of a certain percentage of overhead. The setup of this feature is similar to Cost Allocation but much simpler by design.
-
Reclassification allocates costs when funding agreements are made so that costs not originally reimbursed are reclassified so that they can be reimbursed.
Cost allocations are often a dollar-for-dollar allocation of costs. For example, a check is processed to record telephone expenses to a single chart of account distribution used to initially make such payments, which is the 'pool’ distribution. A variety of programs may be using the telephone service, but at the time of payment it cannot be determined how the expense should be distributed across the various programs. A couple of weeks after the payment an employee FTE assessment is done by program. This information is then defined into the allocation as statistical units from with the Cost Allocation will determine percentages for the allocation. The Cost Allocation system process is run to allocate the costs to the various 'base’ programs from the pool. For example, costs may be allocated as follows:
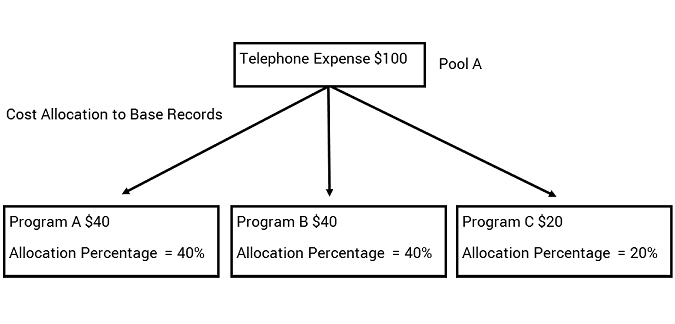
The pool is credited $100 for the expenditure with each program receiving the dollar amount shown above. This is a very simple scenario where the allocation step involves distribution from one pool to three base distributions.