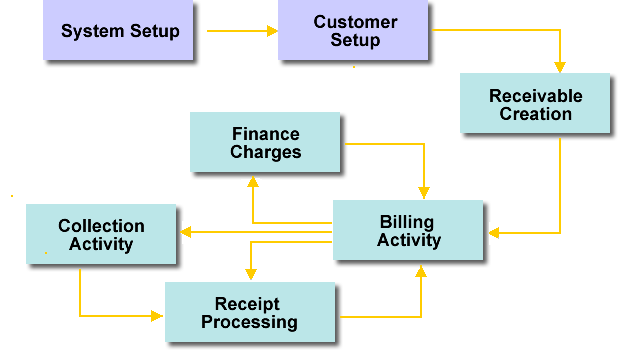
The Accounts Receivable Business Process Life cycle is illustrated as below:

The Accounts Receivable life cycle includes the following seven components:
|
Setting up Accounts Receivable includes setting options on system-wide tables as well as on tables specific to Accounts Receivable. The setup process allows you wide flexibility in configuring your system to meet your needs. |
|
|
A receivable is an accounting event that triggers the billing for goods or services provided or the anticipation of a receipt of money (for example, billing for reimbursement activities, billing a vendor to recover an overpayment to that vendor, or billing an employee or contractor to recoup the unused balance of a monetary advance). Receivables can be modified, reduced, sent to a collection agency, or even completely written off. |
|
|
Billing consists of activities undertaken to collect the money owed for the sale of goods or services, or for money owed related to other types of receivables. Accounts Receivable generates invoices, statements, or both, to bill customers. You can invoke invoice billing either on-demand or through batch processing. Statement billing can only be invoked through batch processing. The billing process also allows you to view generated invoices and statements online, and allows you to reprint bills on-demand or offline. |
|
|
You use the Advantage Financial Cash Receipt (CR) document to record money received and to liquidate a receivable or receivables, where appropriate. The Cash Receipt process supports numerous payment methods, including cash, check, credit card, money order, cashier’s check, payroll deduction, debit card, and electronic funds transfer (EFT). The CR document can also handle previously-recorded checks that are returned for non-sufficient funds, as well as the recording and application of credit balances related to prepayments or overpayments. Once payments have been recorded in Advantage Financial and deposited in the bank, the system provides an automated reconciliation process that compares records received from the bank with the deposit activities recorded in Advantage Financial. As a benefit of this process, cash managers can use the Deposit Reconciliation (DPREC) table for online querying and reporting. |
|
|
If customers are late or delinquent with their payments, finance charges can be automatically applied to their accounts. You can define various finance charges in the form of a flat fee or interest. Multiple fees can be applied to an outstanding receivable. |
|
|
A payment to a vendor is offset and a portion of that payment is retained by the disbursing entity or remitted to a third party. Payments to a vendor may be intercepted on the basis of a Lien, a Tax Levy, a Garnishment, or a Receivable. Payment Intercepts is the process of establishing intercept requests, determining the eligibly of payments for intercept, determining the amount of intercept for individual payments, charging fees on intercepted debt, tracking intercept activity, and transferring funds to the entity requesting the disbursement intercept. The Intercept Functionality in Advantage also allows you to record the Debts that were intercepted in an External Payment System. These Debts could either be an Internal Debt (Debts that originated within the Advantage Application) or an External Debt (Debts that originated outside of the Advantage Application). You can also alert debtors that they may be subject to the intercept process if their payments are not promptly received by issuing Notice of Intent to Intercept Letters. |
|
|
If customers do not pay for the goods and services delivered to them by the due date, Advantage Financial supports numerous approaches for performing collections activities, including:
Most collections activities and record keeping are automated by the system, based on parameters and options you and your entity have previously defined. |